|
Join Surefoot for two FREE and fun storytelling events on Thu 22 Sep in London and Mon 26 Sep in Stirling.
Open to people working within community groups, these engaging events will showcase storytelling techniques to envision and explore positive futures and increase resilience. About the events An exploration of storytelling as a tool that can be effective for guiding groups into thinking about needs and overcoming obstacles. The tools you will learn at this event can be especially useful for those at the forefront of the fight against climate change as a way to envision and explore positive futures and increase resilience in the journey through the difficulties that we all face in the present. Covered during the event:
sign up on eventbrite so we know the numbers for lunch. Book your place Read more and sign up to the event in London, London, Thu 22 Sep 2022, 11:00-3:00 PM Read more and sign up to the event in Stirling Stirling, Mon 26 Sep 2022, 10:00-2:00 PM Project background This initiative is part of the Erasmus+ Once Upon Your Time project . In early 2022, participants from Iceland, Slovenia, Spain and the UK met up for a week’s training. The purpose was to create ways to support young people at risk of social exclusion. The group went through a wide range of exercises to explore Joseph Campbell’s technique Monomyth, also called The Hero’s Journey. As a follow up, Journey to the Inner Hero, Surefoot’s participants share their experiences on how The Hero’s Journey works on body and mind, and reflect on what directions to take with the acquired skills and knowledge.
0 Comments
APPLY NOW! Do you want to improve energy efficiency, thermal comfort AND move to net zero in your community space? HeatHack and The Surefoot Effect are offering a programme for community groups to help plan for the futures of their churches, halls and community centres.
Tackling heat loss and energy efficiency in community buildings, Surefoot working in collaboration with HeatHack is delighted to announce confirmation of an Ingenious Public Engagement Award from the Royal Academy of Engineering. For this project, a small team of people from across Surefoot and HeatHack will be working together to deliver a programme to help UK-based churches and community buildings to understand what a net zero future means for their premises. It will help them not just understand energy efficiency and thermal comfort in difficult buildings, but also to think about how their buildings should be used in their local contexts and how to make this change happen. Groups will emerge from the process with a shared vision, the knowledge and confidence to work well with architects, heating engineers and other professionals, and the evidence of community need that grant funders require. APPLY NOW! We are recruiting community groups and volunteer engineers NOW for sessions starting September – December 2022. Find out more and apply >> More about the programme Key elements
Please contact [email protected] to arrange a conversation about how you can get involved, if you would like to participate either by forming a group or as an assisting engineer. The project is funded by Royal Academy of Engineering Ingenious programme. We recently had a meeting for our Erasmus+ Sustainability, Heritage, and Health project in Athens. Looking out at the Parthenon and thinking about the ecological emergency, Euri had some thoughts:
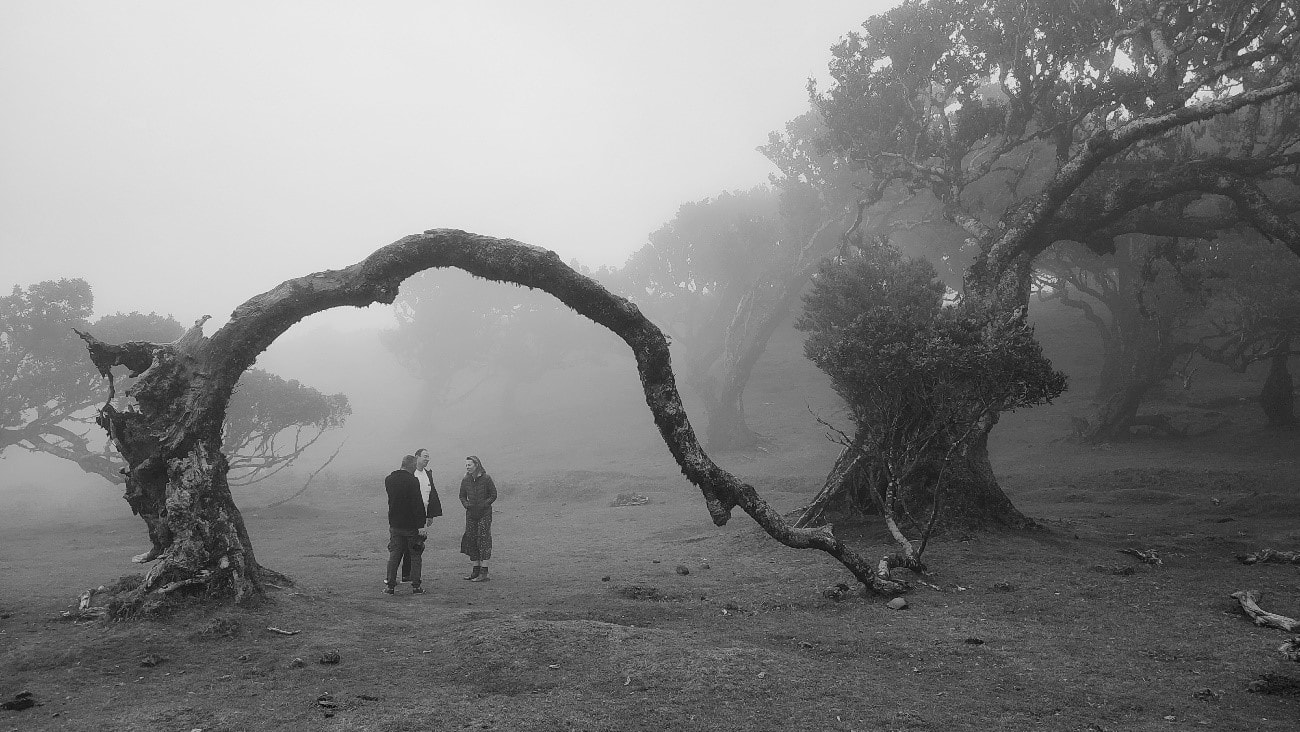
The Parthenon is Greece’s most iconic building, and it is also a symbol of Antiquity and democracy in the world. The building was finished in 438 BC, and it is dedicated to the goddess Athena, after which the ancient city is named. For almost thirteen centuries, the Parthenon overlooked the Athenian city almost untouched. In the final decade of the 6th century AD, the Parthenon was converted into a Christian church dedicated to the Virgin Mary. After the Ottoman conquest, the Parthenon was turned into a mosque in the early 1460s. It was only in 1687 when general Francesco Morosini of the then Republic of Venice invaded the Ottoman-controlled city and bombed the building, where the sitting army had stored gunpowder. One of the architectural marbles of history collapsed in a single event, and with it, a gem of human History. From 1801 to 1803, Earl of Elgin removed some of the surviving sculptures which are now in the British Museum. For most of its history, it was desecrated, forgotten, and ultimately destroyed. It only became celebrated quite recently. The Parthenon is now a symbol of democracy and Western civilisation, celebrated as one of the most important buildings in the world, with millions of tourists visiting every year. Celebrated when it is too late. Does nature have the same fate of the Parthenon? The WWF states that between 1970 and 2016, wildlife populations have declined, on average, by 68%. Terrestrial populations have declined 38%, while freshwater populations have declined by 81%. The rapid loss of species we are seeing today is estimated by experts to be between 1,000 and 10,000 times higher than the natural extinction rate. These experts calculate that between 0.01 and 0.1% of all species will become extinct each year. Will people look back in several hundreds of years and ponder over how could anyone be so reckless and careless as to fail to protect the wealth of the nature world, a symbol of life, unique in the universe? Will people dig up the remains of the natural world like we dig for dinosaur bones today and take them to museums, the only places where people will learn about the massive biodiversity that once thrived on the planet until the 21st Century? Through deforestation, the burning of fossil fuels, land and ocean pollution, mindless consumerism, humanity is stacking up its own gunpowder inside the ancient marvel that is nature and that took billions of years to be what it is today. As we can attest from the history of the Parthenon, it does not take very much for all of it to go away. Will nature be celebrated only when it is gone? Surefoot associate Euri Vidal is working with Abrazo House on a project entitled “Biodiversity Outdoor Learning.” On a recent visit to the Laurisilva forest on the island of Madeira, the eerie forest and the ancient trees showed a picture of the resilience of nature, a resilience in which people may also find inspiration. Laurisilva typifies a previously widespread laurel forest, a gem of the past, which covered much of Southern Europe 15-40 million years ago. The cover in Madeira is the largest surviving area of laurel forest, and it is believed to be 90% primary forest. The forest contains a unique ecosystem of plants and animals, including many endemic species such as the Madeiran long-toed pigeon, and it is for this reason that the forest is a UNESCO protected site. Not only does the forest have a unique biodiversity value, it is also visually compelling. Many of the trees contort, twist, and grow in inexplicable ways and have stood there for thousands of years.
Winds in Madeira are notorious to the extent that pilots need a special training to land on this rocky, mostly solitary island that is seven hundred miles off the coast of Portugal and that rises almost 6,000 feet into the sky. Looking at the trees in this eerie landscape, one can see how the wind has tried to uproot the trees, push them down, and make sure they don’t grow much, possibly for hundreds of years. But you can hear them whisper “This is not over yet.” The trees have managed to withstand the challenge, their roots stubbornly stuck in the ground. Some trees grow horizontally to better cope with the gusts. Or roots have grown wide and deep in case some parts of the root system became weak and died away. You almost see the trees smirking, laughing at the elements, telling the wind, “Come and get me. If you can…” I can’t think of a better way to think of resilience. Determination wins all. When hardship comes your way, be a laurisilva tree. Please see the work Surefoot is currently doing with resilience on Resilience Workshops and Breakthrough for Resilience. Surefoot announces its new free-to-access peer support for people experiencing eco-anxiety. Nothing makes more sense than protecting the planet that gave us all life and everything we have. But, do you find yourself unable to keep going in the face of the relentless dire news about the state of the world? Surefoot’s Eco Anxious Resilient (EAR) Peer Support is a new project which aims to develop free-to-access peer support tools, materials, training and workshops for campaigners, activists and others experiencing eco-anxiety. We will share insights from people who are managing to safeguard their own mental and emotional wellbeing, while also constructively engaging in the fight against global warming and biodiversity loss.
Inspired by the spirit of Glasgow’s 2021 Climate Justice protest and with a £10k grant from The National Lottery Community Fund Scotland - Together for Our Planet programme, EAR Peer Support is funded through to March 2023. Find out more about the EAR Peer Support Project >>> Besides our food-harvest, we also harvest lots of wonderful moments in the forest garden, and we get to know lots of interesting, kind and dedicated people who come and visit us to learn more about forest gardening. Once upon a time – around 10 years ago – I participated in the first online experimentation with Carbon Conversations facilitated by Pam Candea. That was the starting point of a journey that has changed everything in our lives.
After the Carbon Conversation-sessions I considered if I should translate the concept to Danish and started looking for a Danish organisation to team up with – and found the Danish permaculture association. I never translated the concept, and I am not a member of the permaculture association, but I became, together with my husband Steffen, completely engrossed by the concept of forest gardening, which is an integrated part of permaculture. Carbon Conversations covers – as most readers here will know – the fields of energy in houses, transport, food and commodities. I had already worked a lot with the energy-issues both professionally and in our home, but really got caught by the food-issue. At that time, we had a holiday home in the deep forests of Småland in Sweden, where we enjoyed being so much closer to nature – plants, birds, animals, air, water – than in our city-life north of Copenhagen in Denmark. The idea of combining nature with the production of food simply caught us both. Now we have sold the summerhouse and our house in Copenhagen and bought an old farmhouse, still in Småland but a little closer to Denmark and our children and grandchildren. Here we experiment with all the Carbon Conversation-issues – and with extra energy dedicated to the production of our own food, in a plot for annual vegetables as well as in our 1000m2 forest garden. What is a forest garden? A forest garden is a food producing ecosystem that imitates natural ecosystems, being rich in biodiversity and much more resilient than a traditional vegetable garden where you grow annual vegetables like carrots, potatoes and lettuce. In a forest garden you grow a diversity of perennial food crops mixed in a diverse, polyculture system with several storeys. In the top you have trees with fruits and nuts, next storey houses the berries, then comes the larger perennial vegetables and in the bottom, you have cover plants. All mixed with each other to avoid the risks and disadvantages of monocultures – exactly as in the fringe of a forest. In a fully developed forest garden, most plants are perennial. They are part of a balanced and relatively stable ecosystem that doesn’t start from fresh every year. The plants stand stable with their roots deep into the soil where they participate with fungi in an exchange of nutrients and energy. That makes them much more resilient against heat, drought and wind. Most plants in a forest garden are food-producing and the rest are either insect plants or nutrient collectors. Some (most) of them are very pretty as well – but the purpose of a forest garden is not to look good (like in a flower garden). The purpose is to produce food while at the same time supporting biodiversity and carbon sequestration. The polyculture-mixture of trees, bushes and herbs is important for several reasons. Most important is it to create lots of hiding places and lots of different food sources for many different insects. With a very biodiverse food-producing ecosystem, you get a much more resilient system, with lots of predators to balance the number of vermin. Furthermore, biodiversity is decreasing globally, and we should all do our utmost to provide living spaces and food for as many insects, birds and wild animals as possible – also in our food-production. In a forest garden you don’t have naked soil. In a full-grown forest garden, the soil is covered with plants, and in a developing forest garden, we cover the space between plants with organic material. Naked soil is very vulnerable to drought and erosion, and life in the soil – micro-organisms, fungi and bacteria – has much better chances to live and thrive if the ground is covered with either plants or organic material. The soil stays moist and the organic material composts into humus which contributes to the life of both animals and plants. And carbon in the form of CO2 is sequestrated and stored as different carbon-connections in the stems, branches and roots of the plants and the humus in the soil. Our experiences with forest gardening We started developing our forest garden in 2016 and now only six years later we are harvesting lots of fruits, berries and vegetables, from early spring till late fall. We get many visits in the forest garden by people interested in a more sustainable life and food production. You are also welcome – either if you come to Sweden some day or on our website (unfortunately so far only in Danish – but with lots of photos): https://gammelgaard.se/skovhave/ By Christina Meyer |
�
AboutHere’s a collection of some of our articles which have been in our newsletters or published elsewhere.
Archives
May 2024
|
Sign up TO SUREFOOT NEWS >>The Surefoot Effect equips people, communities and organisations with skills for sustainability and resilience.
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed